Leukoplast skin sensitive family - Designed for fragile skin
Frequent dressing changing is a routine practice in wound care. However, each day, injuries are caused through the traumatic removal of traditional dressings, causing unnecessary pain and infections, and higher management costs.
Many patients have sensitive skin. And numbers are growing.
Skin tears are among the most common wounds of elderly patients1. A systematic review reports a general prevalence of up to 22%2. Depending on several factors, the risk for skin damage can be increased1. People with fragile or vulnerable skin such as the elderly or infants, patients on certain medication, with frequent dressing changes or disease-related fragile skin are at higher risk of damage.
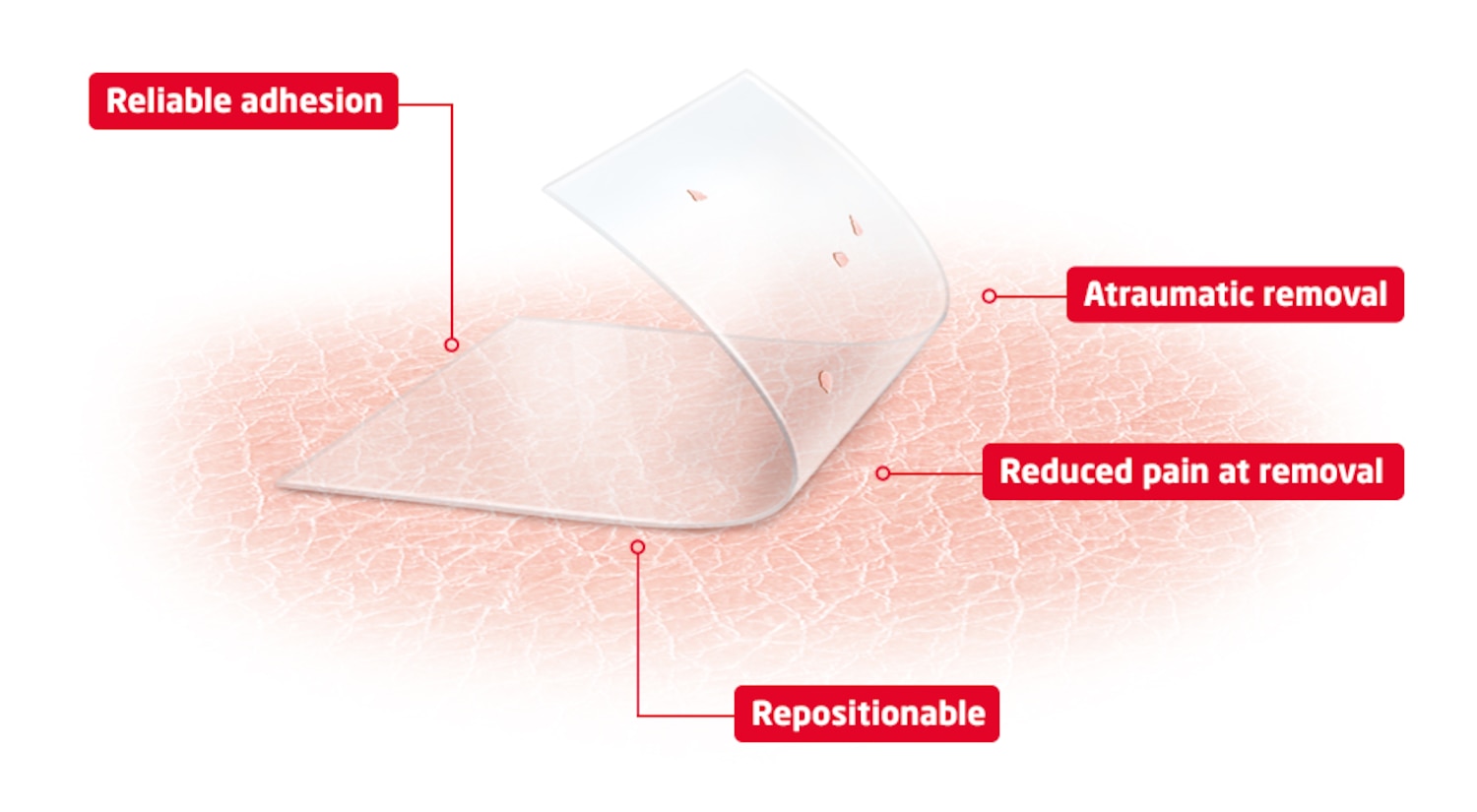
Reliable, loving grip yet gentle removal
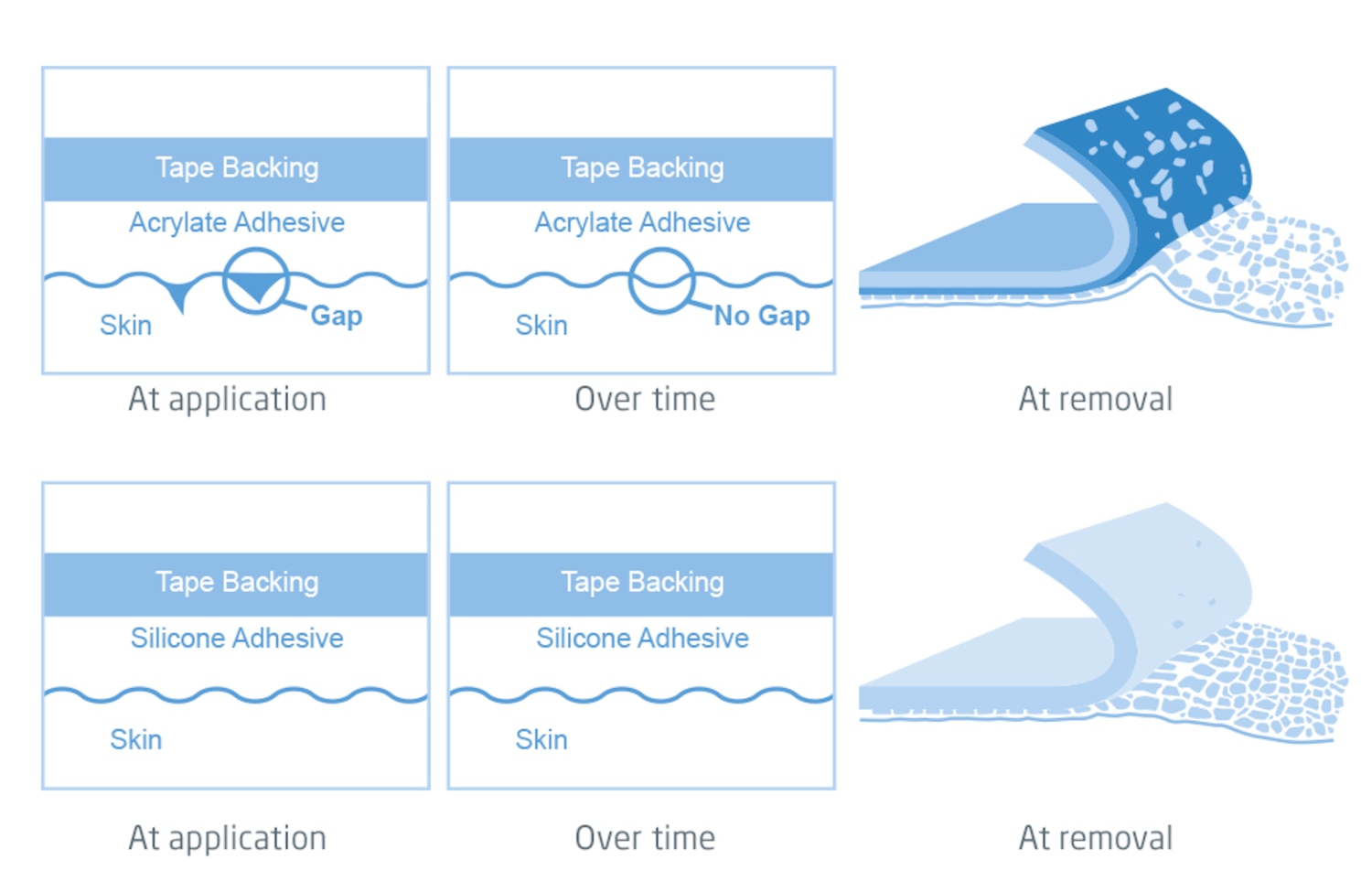
Thanks to the Leukoplast skin sensitive technology using a soft silicone adhesive, the Leukoplast skin sensitive product range offers gentle and secure wound care solutions for highly sensitive or compromised skin surface, while providing an atraumatic and almost pain free removal. Designed for reduced pain and skin damage on removal, the Leukoplast skin sensitive family helps protect fragile skin, while avoiding unnecessary wounds and inflated costs due to increased treatment times and materials.